EVA vs Polyethylene and Polyurethane Foam Mats
Related Product: Foam Kids and Gym Mats Premium 5/8 Inch x 2x2 Ft.
Athletic mats are generally made of one of three popular foam materials - Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA material), Polyethylene or Polyurethane - or a combination of these foam materials. So what's the difference between the foams and why would you choose one over the other?
What is EVA Material made of?
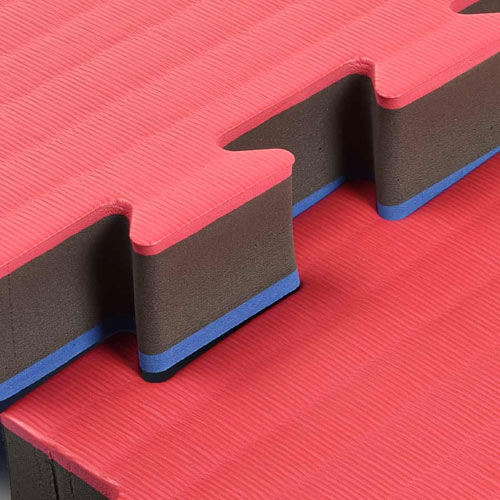
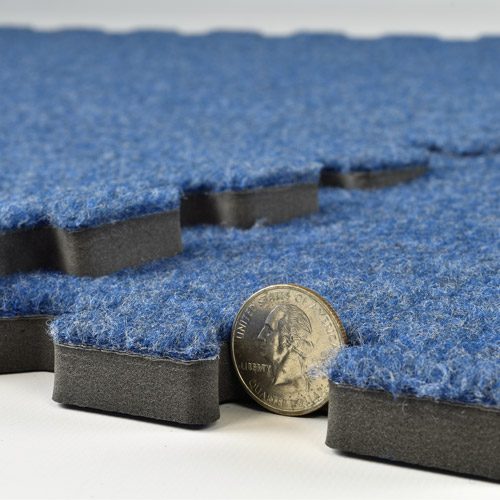
 Ethylene-vinyl acetate, or EVA material, is an elasticized closed-cell foam with rubber-like softness and flexibility. EVA mats will have a glossy appearance and are resistant to UV radiation and cracking. EVA foam is also waterproof.
Ethylene-vinyl acetate, or EVA material, is an elasticized closed-cell foam with rubber-like softness and flexibility. EVA mats will have a glossy appearance and are resistant to UV radiation and cracking. EVA foam is also waterproof.
While the EVA foam does not contain any rubber is is commonly referred to as expanded rubber or foam rubber. EVA Foam is known for its shock absorbing qualities and buoyancy.
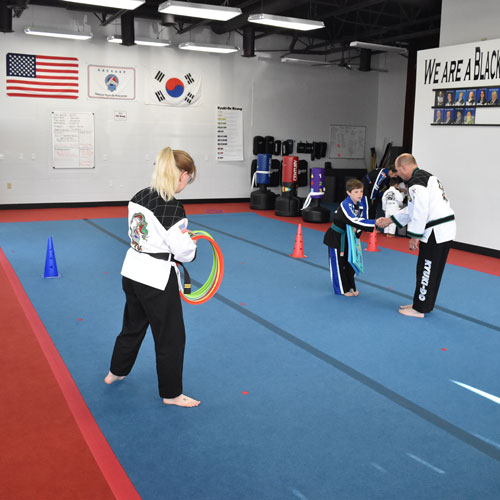
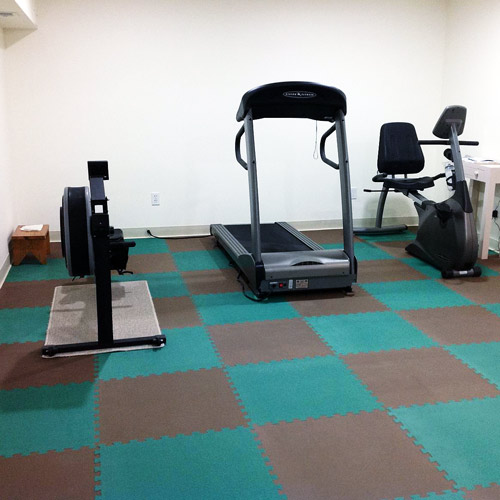
Due to these qualities, EVA material makes an excellent flooring foam for athletic activities as it will absorb impact from falls and can be easily cleaned and disinfected.
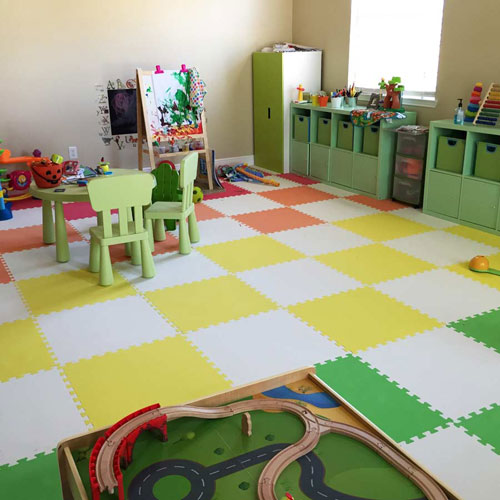
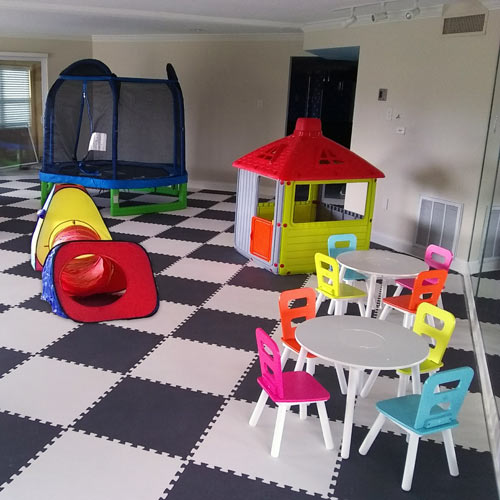
EVA material tiles are popular solution for martial arts facilities, kids play areas, basements, trade shows and much more.
As a closed cell foam, EVA material is firmer than open cell foams and allows for subtle movements when standing on it without much risk rolling ankles. This quality also makes it great as an anti-fatigue flooring material.
PE Foam Mats
 Polyethylene, or PE, is the most common plastic available today. If often feels waxy to the touch and carries high impact strength, meaning it can absorb a lot of energy before rupture. It's also very ductile, meaning can easily deform under tensile stress.
Polyethylene, or PE, is the most common plastic available today. If often feels waxy to the touch and carries high impact strength, meaning it can absorb a lot of energy before rupture. It's also very ductile, meaning can easily deform under tensile stress.
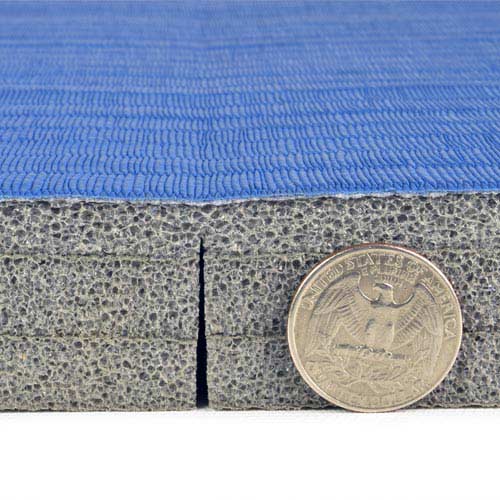
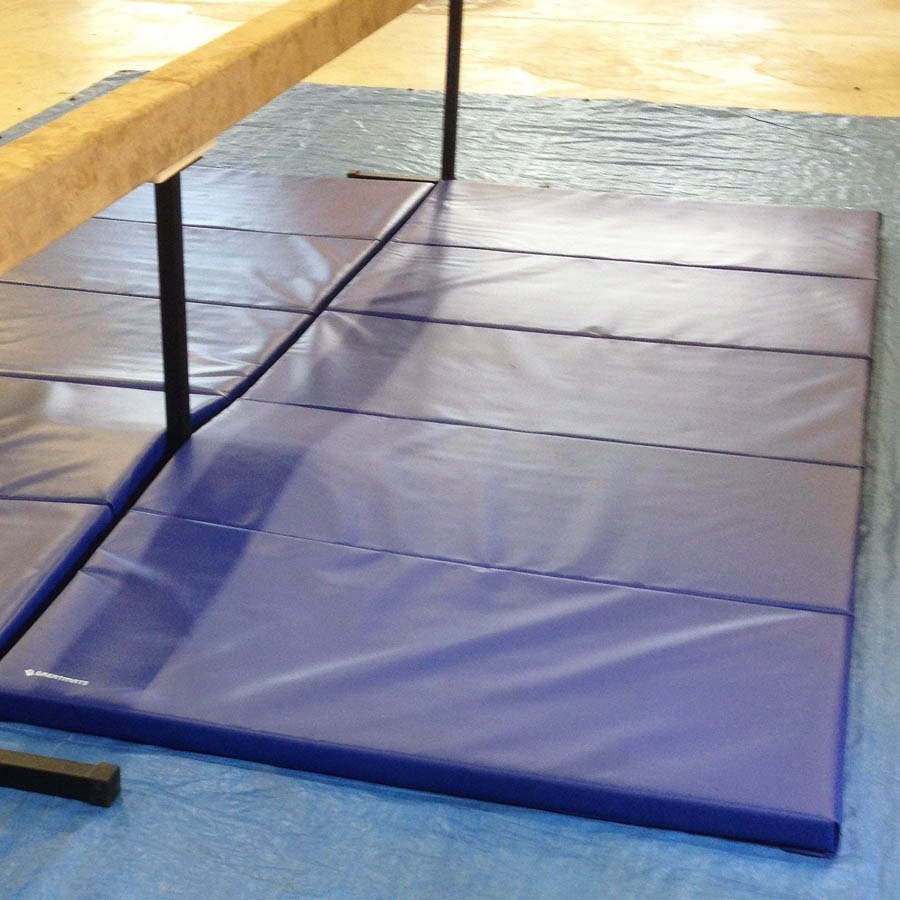
When used as a foam flooring or matting material, PE is often cross-linked, creating a fine, closed-cell foam that is unaffected by mildew, mold, rot and bacteria and provides firm material with excellent strength and shock absorption. That doesn't necessarily mean it will be soft landing if you fall hard in this foam as the energy is contained to a relatively small area and not broadly distributed.
 Cross linking makes the foam more rigid and helps it rebound quickly to its original shape when stretched or squished, giving it more bounce than other foams.
Cross linking makes the foam more rigid and helps it rebound quickly to its original shape when stretched or squished, giving it more bounce than other foams.
The closed cell foam is also an excellent thermal insulator.
This is a common foam for thicker versions of foam flooring as it is much lighter weight than most other alternatives.
The foam itself is not ideal as a finished surface as it can easily by punctured, gouged or cut, which is why it is often wrapped in vinyl or has a vinyl or carpet bonded surface.
You'll often find PE foam in folding or roll-out cheerleading, gymnastics or grappling mats or as a foam underlayments.
PU Foam Mats
 Polyurethane, or PU, is an open cell foam best known for providing extreme cushion. As air is allowed to flow through the foam, it enables the foam to create a much softer and giving surface.
Polyurethane, or PU, is an open cell foam best known for providing extreme cushion. As air is allowed to flow through the foam, it enables the foam to create a much softer and giving surface.
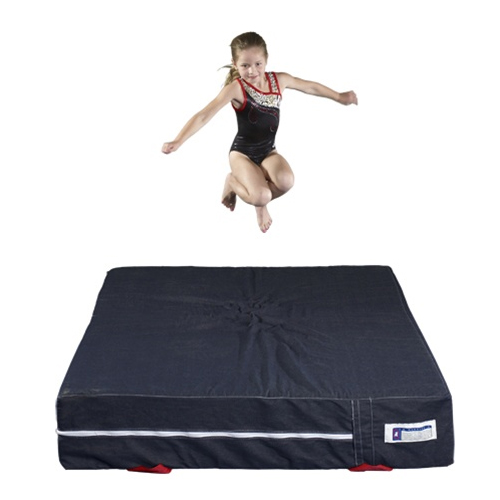
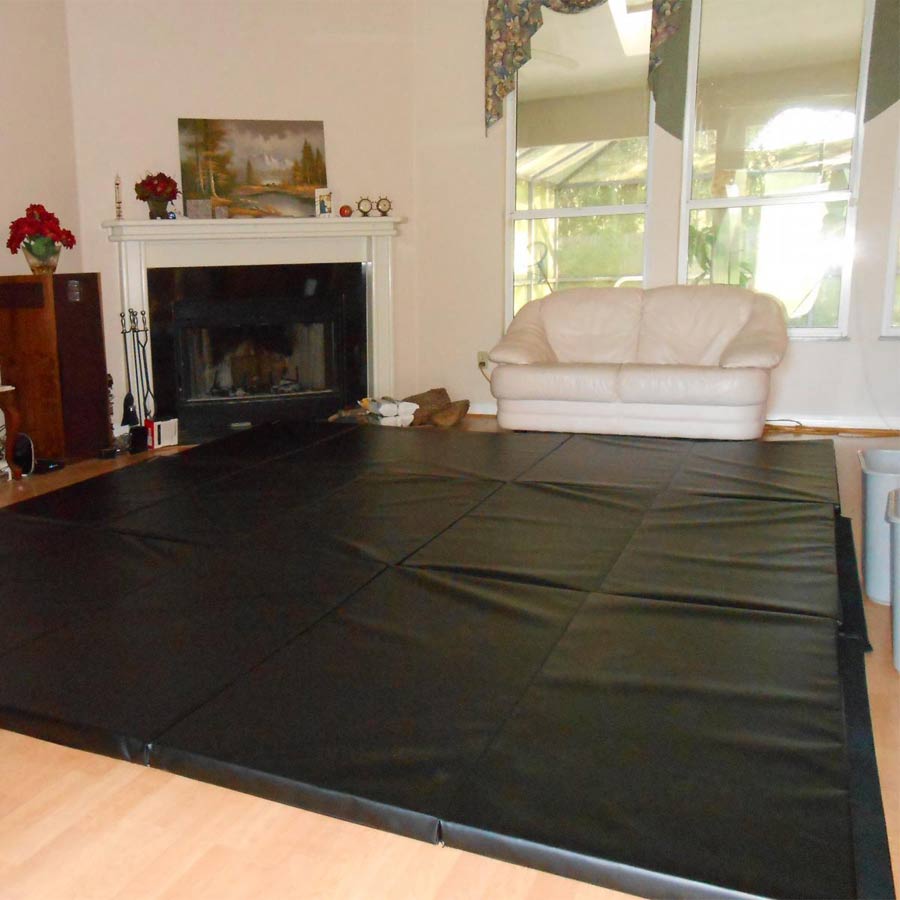
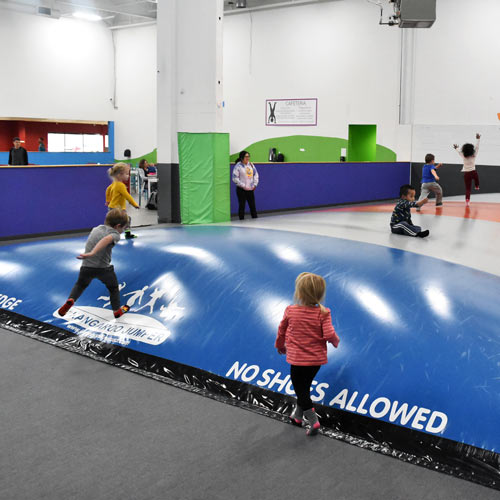
Polyurethane foam is superior to other foams at absorbing energy, but lacks some in the stability department. This foam is used in much thicker mats designed for high impact landings, such as crash pads due to its broad distribution of energy.
The same features that make it excellent for absorbing impact and distributing energy also make it less desirable for walking, running or jumping as it simply crushes and collapses underfoot instead of springing back or providing resistance.
You'll often find this foam in landing pads or fluff mats as they help take the sting out of falls or landing on your body, rather than springing off your feet or hands.
Like PE foam, PU Foam is not ideal for use on its own and needs to be wrapped with another durable surface, such as vinyl or denim.
When choosing your foam flooring, make sure you keep in mind how much spring, firmness or energy absorption you'll need as well as how easy it will be to clean and disinfect.